堆排序与快速排序,归并排序一样都是时间复杂度为O(N*logN)的几种常见排序方法。
二叉堆的定义
二叉堆是完全二叉树或者是近似完全二叉树。
二叉堆满足二个特性:
- 父结点的键值总是大于或等于(小于或等于)任何一个子节点的键值。
- 每个结点的左子树和右子树都是一个二叉堆(都是最大堆或最小堆)。
当父结点的键值总是大于或等于任何一个子节点的键值时为最大堆。当父结点的键值总是小于或等于任何一个子节点的键值时为最小堆。下图展示一个最小堆:
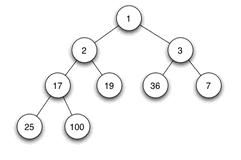
由于其它几种堆(二项式堆,斐波纳契堆等)用的较少,一般将二叉堆就简称为堆。
堆的存储
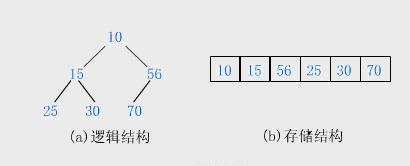
一般都用数组来表示堆,
方法一
数组的下标从 0 开始。i 结点的父结点下标就为 (i – 1) / 2。它的左右子结点下标分别为 2 * i + 1 和 2 * i + 2。如第 0 个结点左右子结点下标分别为 1 和 2。 如下图:
方法二
数组的下标从1开始。根节点下标就是1。
i节点的父节点下标就是 i/2 。
左子节点下标是 2 * i 。
右子节点下标是 2 * i + 1 。
Code
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "MaxHeap.h"
int main()
{
printf("max heap test\n");
int iSize = 10;
int aiHeap[] = {0,4,1,3,2,16,9,10,14,8,7};
int * piHeap = &aiHeap[1];
CMaxHeap oMaxHeap;
printf("int aiHeap[] = {0,4,1,3,2,16,9,10,14,8,7};\n");
oMaxHeap.m_vArrayToHeap(piHeap, iSize);
for (int i=1; i<=iSize; i++)
{
printf("%d ", aiHeap[i]);
}
printf("\n");
printf("m_vDisplay(): \n");
oMaxHeap.m_vDisplay();
printf("\n");
CMaxHeap oMaxHeap2;
oMaxHeap2.m_bInsertData(1);
oMaxHeap2.m_bInsertData(2);
oMaxHeap2.m_bInsertData(4);
oMaxHeap2.m_bInsertData(5);
oMaxHeap2.m_bInsertData(0);
oMaxHeap2.m_bInsertData(100);
oMaxHeap2.m_bInsertData(7);
oMaxHeap2.m_bInsertData(8);
oMaxHeap2.m_bInsertData(0);
oMaxHeap2.m_bInsertData(9);
printf("m_vDisplay(): \n");
oMaxHeap2.m_vDisplay();
printf("m_vDeleteRoot(): \n");
oMaxHeap2.m_vDeleteRoot();
oMaxHeap2.m_vDisplay();
printf("m_vHeapSort(): \n");
oMaxHeap2.m_vHeapSort();
oMaxHeap2.m_vDisplay();
printf("Done\n");
return 0;
}
#ifndef HEAP_H
#define HEAP_H
const int DEFAULT_HEAP_LENGTH = 100000;
class CMaxHeap
{
public:
/* @brief ctor
* @param iLength: the size of array memory.
*/
CMaxHeap(int iLength = DEFAULT_HEAP_LENGTH);
/*
* @brief dtor
*/
virtual ~CMaxHeap();
/* @brief build heap with the data in piArray, and then, copy the heap
* data back to piArray.
* @param piArray[in][out]:
* piArray must be start piArray[1].
* if piArray[1...9], the data is from piArray[1]->piArray[9],
* so iArraySzie=9
* @param iArraySize: the size of piArray.
*/
void m_vArrayToHeap(int * piArray, int iArraySize);
bool m_bInsertData(int iData);
void m_vDeleteRoot();
void m_vBuildMaxHeap();
void m_vDisplay();
int m_iGetRoot();
bool m_bIsEmpty();
void m_vHeapSort();
private:
/* @brief it assume the child of i is already MaxHeap.
* and it will build the new MaxHeap with i, leftChild(i), rightChild(i).
*/
void m_vMaxHeapify(int i);
void vSwap(int & iA, int & iB);
int m_iParentIndex(int i);
int m_iLeftChildIndex(int i);
int m_iRightChildIndex(int i);
/*
* @brief m_piHeapArray is start from array[0], but use from array[1]
* so you must be very careful to use it.
*/
int * m_piHeapArray;
/* the data number in Heap array.
* if the m_iHeapSize=10, it means the heapArray index
* start from m_piHeapArray[1], end with m_piHeapArray[10].
*/
int m_iHeapSize;
//allocated memory of Heap array
int m_iHeapLength;
};
#endif
/*
A[1...n]
1.
A[n/2+1], A[n/2+2], ... , A[n] all is the leaf of this tree
2.
A[1], A[2], ..., A[n/2] all is not the leaf of this tree
3.
the height of this tree is floor(log(n)).
note: floor(3.2)=3, and ceil(3.2)=4 .
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "MaxHeap.h"
CMaxHeap::CMaxHeap(int iLength) :
m_iHeapSize(0)
{
m_piHeapArray = new int[iLength + 1];
m_iHeapLength = iLength;
}
CMaxHeap::~CMaxHeap()
{
delete[] m_piHeapArray;
}
int
CMaxHeap::m_iGetRoot()
{
return m_piHeapArray[1];
}
bool
CMaxHeap::m_bIsEmpty()
{
return (m_iHeapSize == 0);
}
void
CMaxHeap::m_vDisplay()
{
for (int i=1; i<=m_iHeapSize; i++)
{
printf("%d ", m_piHeapArray[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
void
CMaxHeap::m_vArrayToHeap(int * piArray, int iArraySize)
{
if(iArraySize > m_iHeapLength)
{
printf("input iArraySize is too large\n");
return ;
}
m_iHeapSize = iArraySize;
memcpy(m_piHeapArray+1, piArray, iArraySize*sizeof(int));
m_vBuildMaxHeap();
memcpy(piArray, m_piHeapArray+1, iArraySize*sizeof(int));
}
bool
CMaxHeap::m_bInsertData(int iData)
{
if(m_iHeapSize+1 > m_iHeapLength)
{
printf("the memory of heap array is not enough.\n");
return false;
}
m_iHeapSize++;
m_piHeapArray[m_iHeapSize] = iData;
m_vBuildMaxHeap();
}
void
CMaxHeap::m_vDeleteRoot()
{
if(m_iHeapSize == 0)
{
printf("there is no data in heap array.\n");
return ;
}
m_piHeapArray[1] = m_piHeapArray[m_iHeapSize];
m_iHeapSize--;
m_vBuildMaxHeap();
}
void
CMaxHeap::m_vBuildMaxHeap()
{
for (int i=m_iHeapSize/2; i>=1; i--)
{
m_vMaxHeapify(i);
}
}
void
CMaxHeap::m_vMaxHeapify(int i)
{
int iLeftChildIndex = m_iLeftChildIndex(i);
int iRightChildIndex = m_iRightChildIndex(i);
int iLargestIndex = 0;
if(iLeftChildIndex <= m_iHeapSize &&
m_piHeapArray[iLeftChildIndex] > m_piHeapArray[i])
{
iLargestIndex = iLeftChildIndex;
}
else
{
iLargestIndex = i;
}
if(iRightChildIndex <= m_iHeapSize &&
m_piHeapArray[iRightChildIndex] > m_piHeapArray[iLargestIndex])
{
iLargestIndex = iRightChildIndex;
}
if(iLargestIndex != i)
{
vSwap(m_piHeapArray[i], m_piHeapArray[iLargestIndex]);
m_vMaxHeapify(iLargestIndex);
}
}
void
CMaxHeap::m_vHeapSort()
{
int iHeapSizeTemp = m_iHeapSize;
for (int i=m_iHeapSize; i>=2; i--)
{
vSwap(m_piHeapArray[1], m_piHeapArray[i]);
m_iHeapSize--;
m_vMaxHeapify(1);
}
m_iHeapSize = iHeapSizeTemp; //but now, m_iHeapSize just stand for the number of data.
}
void
CMaxHeap::vSwap(int & iA, int & iB)
{
int iT = iA;
iA = iB;
iB = iT;
}
inline int
CMaxHeap::m_iParentIndex(int i)
{
return i/2;
}
inline int
CMaxHeap::m_iLeftChildIndex(int i)
{
return 2*i;
}
inline int
CMaxHeap::m_iRightChildIndex(int i)
{
return 2*i+1;
}