终于看懂了,哈哈。感谢这位兄弟。
http://blog.csdn.net/dapengbusi/article/details/7463968
问题描述
给定n种物品和一背包。物品i的重量是wi,其价值为vi,背包的容量为C。问应如何选择装入背包的物品,使得装入背包中物品的总价值最大?
对于一种物品,要么装入背包,要么不装。所以对于一种物品的装入状态可以取0和1.我们设物品i的装入状态为xi,xi∈ (0,1),此问题称为0-1背包问题。
举例分析
数据:
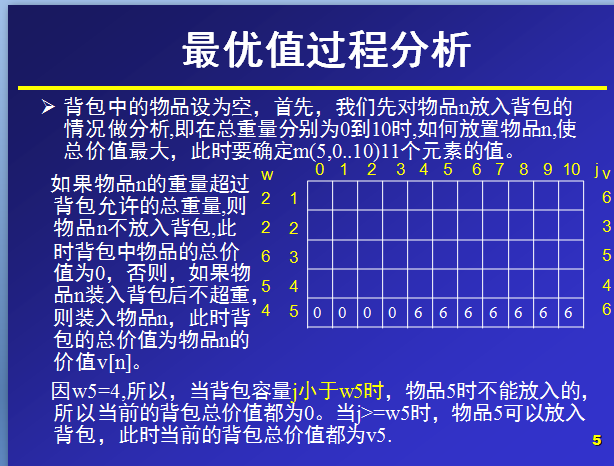
物品个数n=5,
物品重量w[n]={0,2,2,6,5,4},
物品价值V[n]={0,6,3,5,4,6},
(第0位,置为0,不参与计算,只是便于与后面的下标进行统一,无特别用处,也可不这么处理。)
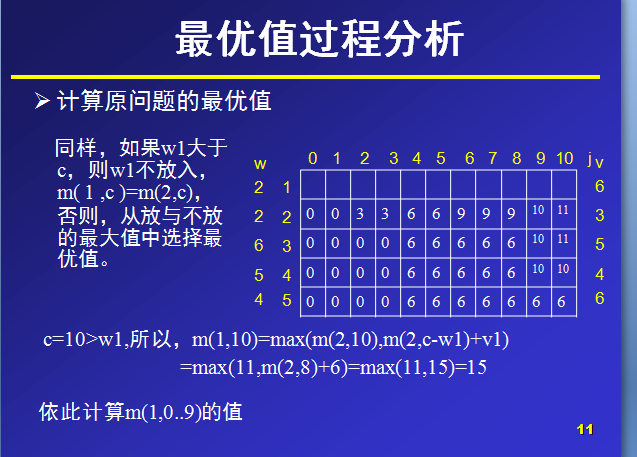
总重量c=10.
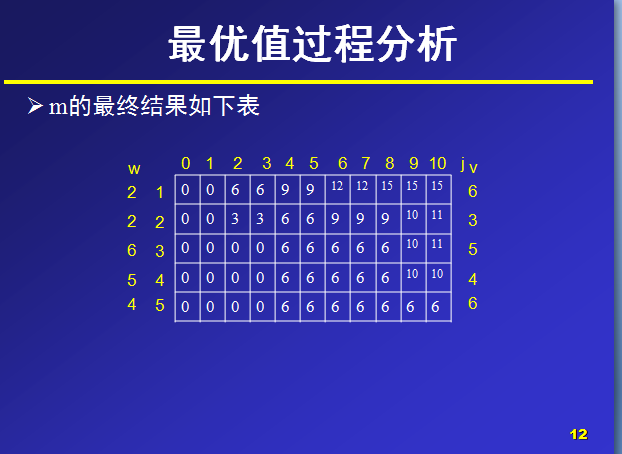
Ø背包的最大容量为10,那么在设置数组m大小时,可以设行列值为6和11,
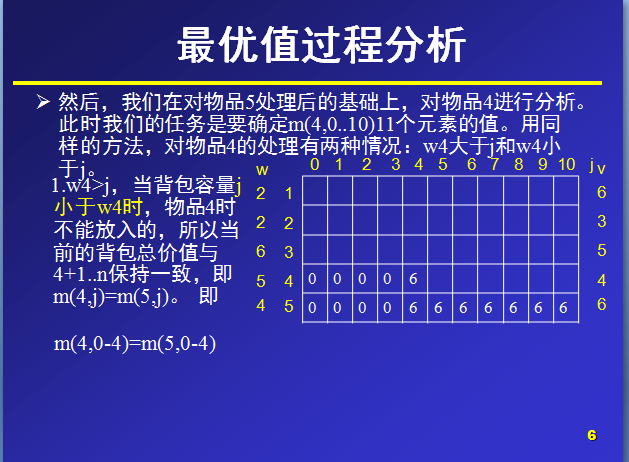
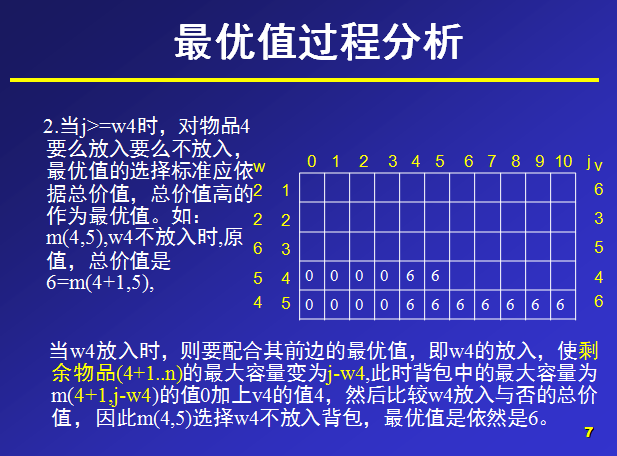
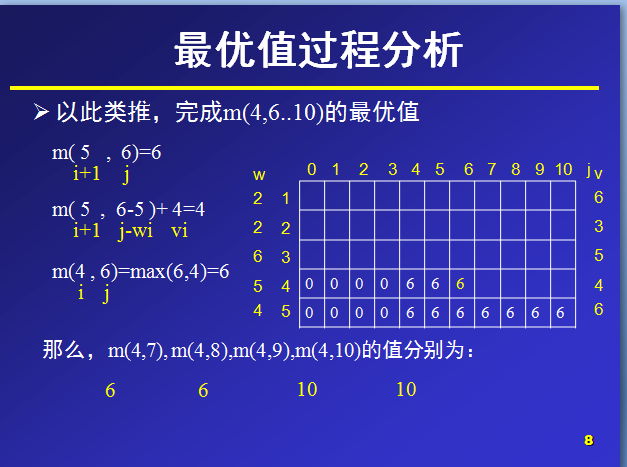
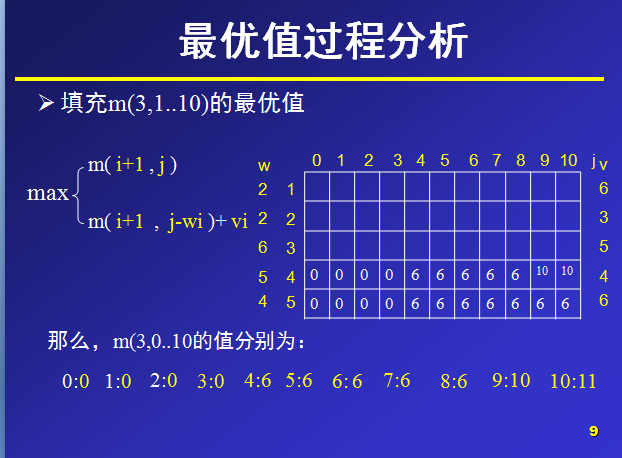
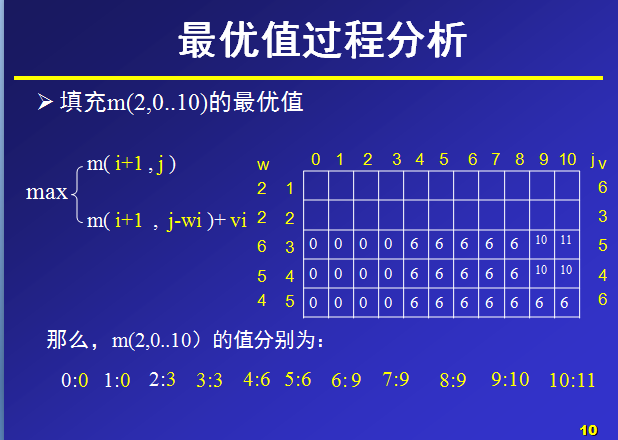
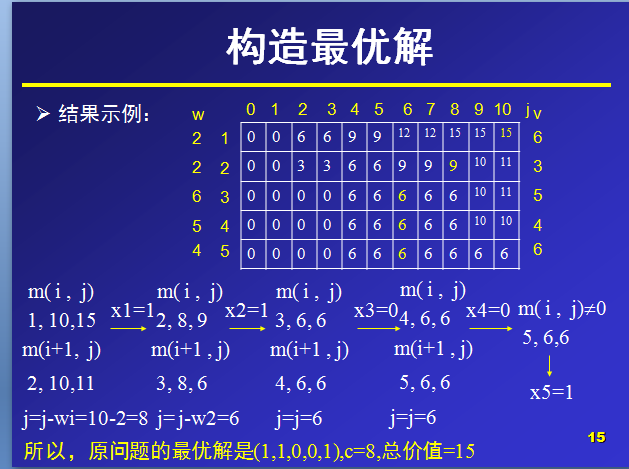
那么,对于m(i,j)就表示可选物品为i…n背包容量为j(总重量)时背包中所放物品的最大价值。





#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
using namespace std;
int iMax(int a, int b) {
return a > b ? a : b;
}
/*
* @param iCapacity: the bag's capacity.
* @param piWeight: the array of obj's weight.
* @param piValue: the value of obj's value.
* @param iObjNum: the number of objs.
* @param [out]ppResult: the result.
* @return the max value the bag can hold.
*/
int iBag(
const int iCapacity,
const int * piWeight,
const int * piValue,
const int iObjNum,
int **ppResult)
{
int i;
int j;
for (i = 0; i <= iCapacity; i++) {
ppResult[iObjNum][i] = (i < piWeight[iObjNum]) ? 0 : piValue[iObjNum];
}
for (i = iObjNum-1; i >= 1; i--)
{
for (j = 0; j <= iCapacity; j++)
{
if (j < piWeight[i])
{
ppResult[i][j] = ppResult[i+1][j];
}
else
{
ppResult[i][j] = iMax(ppResult[i+1][j], piValue[i] + ppResult[i+1][j-piWeight[i]]);
}
}
}
return ppResult[1][iCapacity];
}
void answer(
int iCapacity,
const int n,
const int w[],
int **m,
int x[])
{
int j = iCapacity;
int i;
for (i = 1; i <= n-1; i++)
{
if(m[i][j] == m[i+1][j])
{
x[i] = 0;
}
else
{
x[i] = 1;
j = j - w[i];
}
}
x[n] = m[i][j] ? 1 : 0;
}
int main()
{
int i,j;
int c = 10;
int w[] = {0, 2, 2, 6, 5, 4};
int v[] = {0, 6, 3, 5, 4, 6};
int n = sizeof(w)/sizeof(w[0]) - 1;
int ** m = (int**)malloc(sizeof(int*)*6);
for (i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
m[i] = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*11);
}
int iResult = iBag(c, w, v, n, m);
printf("iBag = %d\n", iResult);
for (int i = 0; i <= 5; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <= 10; j++) {
printf("%2d ", m[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
int aiResult[100] = {0};
answer(c, n, w, m, aiResult);
for (int k = 1; k <= 5; k++)
{
printf("%d ", aiResult[k]);
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
}