Welcome to MDGSF's Blog!
This is my github blog-
[算法学习][leetcode] 3 Longest Substring without Repeating Characters
https://leetcode.com/problems/longest-substring-without-repeating-characters/description/
题目
Given a string, find the length of the longest substring without repeating characters.
Examples:
Given “abcabcbb”, the answer is “abc”, which the length is 3.
Given “bbbbb”, the answer is “b”, with the length of 1.
Given “pwwkew”, the answer is “wke”, with the length of 3. Note that the answer must be a substring, “pwke” is a subsequence and not a substring.
题目翻译
题目解析
参考答案
#include <iostream> #include <map> #include <set> #include <stdio.h> using namespace std; class Solution { public: int lengthOfLongestSubstring(string s) { int iLen = s.length(); int iMaxSubLen = 0; int iSubLen = 0; int iSubStart = 0; int iSubEnd = 0; set<char> setCurSubCharacter; set<char>::iterator iter; for (int i = 0; i < iLen; i++) { char c = s[i]; if(setCurSubCharacter.size() == 0) { setCurSubCharacter.insert(c); iSubStart = i; iSubEnd = i; iSubLen = 1; if(iSubLen > iMaxSubLen) { iMaxSubLen = iSubLen; } } else { iter = setCurSubCharacter.find(c); if(iter != setCurSubCharacter.end()) { iSubEnd++; while(1) { if(s[iSubStart] == c) { ++iSubStart; break; } else { setCurSubCharacter.erase(s[iSubStart]); ++iSubStart; } } iSubLen = iSubEnd - iSubStart + 1; if(iSubLen > iMaxSubLen) { iMaxSubLen = iSubLen; } } else { setCurSubCharacter.insert(c); iSubEnd++; iSubLen++; if(iSubLen > iMaxSubLen) { iMaxSubLen = iSubLen; } } } } return iMaxSubLen; } }; int main() { string s = "dvdf"; Solution o; int iRet = o.lengthOfLongestSubstring(s); return 0; }
-
[Windows] VSCode 添加Code Snippets
文件 –> 首选项 –> 用户代码片段
然后选择C++
cpp.json
{ /* // Place your snippets for C here. Each snippet is defined under a snippet name and has a prefix, body and // description. The prefix is what is used to trigger the snippet and the body will be expanded and inserted. Possible variables are: // $1, $2 for tab stops, $0 for the final cursor position, and ${1:label}, ${2:another} for placeholders. Placeholders with the // same ids are connected. // Example: "Print to console": { "prefix": "log",, "body": [ "console.log("$1");", "$2" ], "description": "Log output to console" } */ "#ifndef … #define … #endif":{ "prefix": "def", "body": "#ifndef ${1:SYMBOL}\n#define $1 ${2:value}\n#endif\t// ${1:SYMBOL}" }, "#include <>":{ "prefix": "Inc", "body": "#include <${1:.h}>" }, "#include \"\"":{ "prefix": "inc", "body": "#include \"${1:.h}\"" }, "#pragma mark":{ "prefix": "mark", "body": "#if 0\n${1:#pragma mark -\n}#pragma mark $2\n#endif\n\n$0" }, "main()":{ "prefix": "main", "body": "int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) {\n\t$1\n\treturn 0;\n}" }, "For Loop":{ "prefix": "for", "body": "for (${1:i} = 0; ${1:i} < ${2:count}; ${1:i}${3:++}) {\n\t$4\n}" }, "Define and For Loop":{ "prefix": "dfor", "body": "size_t ${1:i};\nfor (${1:i} = ${2:0}; ${1:i} < ${3:count}; ${1:i}${4:++}) {\n\t$5\n}" }, "Header Include-Guard":{ "prefix": "once", "body": "#ifndef ${1:SYMBOL}\n#define $1\n\n${2}\n\n#endif /* end of include guard: $1 */\n" }, "Typedef":{ "prefix": "td", "body": "typedef ${1:int} ${2:MyCustomType};" }, "Typedef Struct":{ "prefix": "tst", "body": "typedef struct ${1:StructName} {\n\t$2\n}${3:MyCustomType};" }, "Do While Loop":{ "prefix": "do", "body": "do {\n\t$0\n} while($1);" }, "While Loop":{ "prefix": "while", "body": "while ($1) {\n\t$2\n}" }, "fprintf":{ "prefix": "fprintf", "body": "fprintf(${1:stderr}, \"${2:%s}\\\\n\", $3);$4" }, "If Condition":{ "prefix": "if", "body": "if ($1)\n{\n\t$2\n}" }, "If Else":{ "prefix": "ife", "body": "if ($1) {\n\t$2\n} else {\n\t$3\n}" }, "If ElseIf":{ "prefix": "iff", "body": "if ($1) {\n\t$2\n} else if ($3) {\n\t$4\n}" }, "If ElseIf Else":{ "prefix": "iffe", "body": "if ($1) {\n\t$2\n} else if ($3) {\n\t$4\n} else {\n\t$5\n}" }, "Switch Statement":{ "prefix": "sw", "body": "switch ($1) {\n$2default:\n\t${3:break;}\n}$0" }, "case break":{ "prefix": "cs", "body": "case $1:\n{\n\t$2\n}\nbreak;\n$0" }, "printf":{ "prefix": "printf", "body": "printf(\"${1:%s }\\n\", $2);$3" }, "scanf":{ "prefix": "scanf", "body": "scanf(\"${1:%s}\\n\", $2);$3" }, "Struct":{ "prefix": "st", "body": "struct ${1:name_t} {\n\t$2\n};" }, "void":{ "prefix": "void", "body": "void ${1:name}($2) {\n\t$3\n}" }, "any function":{ "prefix": "func", "body": "${1:int} ${2:name}($3) {\n\t$5\n\treturn ${4:0};\n}" }, "write file":{ "prefix": "wf", "body": "FILE *${1:fp};\n${1:fp} = fopen (\"${2:filename.txt}\",\"w\");\nif (${1:fp}!=NULL)\n{\n\tfprintf(${1:fp},\"${3:Some String\\\\n}\");\n\tfclose (${1:fp});\n}" }, "read file":{ "prefix": "rf", "body": "FILE *${1:fp};\n${1:fp} = fopen (\"${2:filename.txt}\",\"r\");\nif (${1:fp}!=NULL)\n{\n\tfscanf(${1:fp},\"${3:Some String\\\\n}\", ${3:&var});\n\tfclose (${1:fp});\n}", "description": "read file opeartion including fopen, fscanf and fclose." }, "Enumeration":{ "prefix": "enum", "body": "enum ${1:name} { $0 };" }, "Class":{ "prefix": "cl", "body": "class ${1:name_t} {\nprivate:\n\t${0:/* data */}\n\npublic:\n\t${1:name_t} (${2:arguments});\n\tvirtual ~${1:name_t} ();\n};" }, "Namespace":{ "prefix": "ns", "body": "namespace ${1:name} {\n\t$2\n} /* $1 */" }, "cout":{ "prefix": "cout", "body": "std::cout << \"${1:/* message */}\" << \"\\\\n\";" }, "cin":{ "prefix": "cin", "body": "std::cin >> ${1:/* variable */};" }, "cerr":{ "prefix": "cerr", "body": "std::cerr << \"${1:/* error message */}\" << \"\\\\n\";" }, "std::map":{ "prefix": "map", "body": "std::map<${1:key}, ${2:value}> map$3;" }, "std::string":{ "prefix": "str", "body": "std::string" }, "std::vector":{ "prefix": "vector", "body": "std::vector<${1:int}> v$2;" }, "template <typename>":{ "prefix": "tp", "body": "template <typename ${1:T}>" } }
-
[算法学习][leetcode] 2 Add Two Numbers
https://leetcode.com/problems/add-two-numbers/
题目
You are given two non-empty linked lists representing two non-negative integers. The digits are stored in reverse order and each of their nodes contain a single digit. Add the two numbers and return it as a linked list.
You may assume the two numbers do not contain any leading zero, except the number 0 itself.
Input: (2 -> 4 -> 3) + (5 -> 6 -> 4) Output: 7 -> 0 -> 8
题目翻译
题目解析
参考答案
#include <iostream> #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> using namespace std; struct ListNode { int val; ListNode *next; ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} }; // Input: (2 -> 4 -> 3) + (5 -> 6 -> 4) // Output: 7 -> 0 -> 8 class Solution { public: ListNode *addTwoNumbers(ListNode *l1, ListNode *l2) { ListNode * pHead = NULL; ListNode * pTail = NULL; int iFlag = 0; while (l1 != NULL && l2 != NULL) { int iNum = l1->val + l2->val; iNum += iFlag; if (iNum >= 10) { iNum -= 10; iFlag = 1; } else { iFlag = 0; } ListNode * pNewNode = new ListNode(iNum); if(pHead == NULL) { pHead = pNewNode; pTail = pNewNode; } else { pTail->next = pNewNode; pTail = pNewNode; } l1 = l1->next; l2 = l2->next; } while(l1 != NULL) { int iNum = l1->val; iNum += iFlag; if (iNum >= 10) { iNum -= 10; iFlag = 1; } else { iFlag = 0; } ListNode * pNewNode = new ListNode(iNum); if(pHead == NULL) { pHead = pNewNode; pTail = pNewNode; } else { pTail->next = pNewNode; pTail = pNewNode; } l1 = l1->next; } while(l2 != NULL) { int iNum = l2->val; iNum += iFlag; if (iNum >= 10) { iNum -= 10; iFlag = 1; } else { iFlag = 0; } ListNode * pNewNode = new ListNode(iNum); if(pHead == NULL) { pHead = pNewNode; pTail = pNewNode; } else { pTail->next = pNewNode; pTail = pNewNode; } l2 = l2->next; } if(iFlag == 1) { ListNode * pNewNode = new ListNode(1); pTail->next = pNewNode; pTail = pNewNode; } return pHead; } }; int main() { return 0; }
-
[算法学习][leetcode] 1 Two Sum
求和系列题目
链接
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/two-sum/
https://leetcode.com/problems/two-sum/description/
题目
Given an array of integers, return indices of the two numbers such that they add up to a specific target.
You may assume that each input would have exactly one solution, and you may not use the same element twice.
Example: Given nums = [2, 7, 11, 15], target = 9,
Because nums[0] + nums[1] = 2 + 7 = 9,
return [0, 1].
题目翻译
给定一个整数数组 nums 和一个目标值 target,请你在该数组中找出和为目标值的那 两个 整数,并返回他们的数组下标。
你可以假设每种输入只会对应一个答案。但是,你不能重复利用这个数组中同样的元素。
示例:
给定 nums = [2, 7, 11, 15], target = 9
因为 nums[0] + nums[1] = 2 + 7 = 9
所以返回 [0, 1]
题目解析
方法一:暴力法
暴力求解,两重循环,遍历所有的可能性。时间复杂度 O(n^2)。
这个太慢了,会超出时间限制。
class Solution: def twoSum(self, nums: List[int], target: int) -> List[int]: for i, iv in enumerate(nums): j = i + 1 while j < len(nums): if nums[i] + nums[j] == target: return [i, j] j += 1方法二:两头逼近法
先排个序,然后从数组的两端向中间逼近。
排序时间复杂度 O(nlogn)。逼近过程复杂度 O(n)
所以复杂度为 O(nlogn + n) = O(nlogn)
这题目要求返回的是下标,所以这种方法排序的时候下标就改变了。如果在把下标记录下来,就不是很方便了。
如果要求返回的是值的话,可以这么写:
class Solution: def twoSum(self, nums: List[int], target: int) -> List[int]: nums.sort() start = 0 end = len(nums) - 1 while start < end: if nums[start] + nums[end] == target: return [nums[start], nums[end]] elif nums[start] + nums[end] > target: end -= 1 else: start += 1方法三:查找哈希表
遍历一次,时间复杂度为 O(n),分析如下。
nums = [2, 7, 11, 15], target = 9
先建立一个空的哈希表 d
遍历到 2 的时候,计算 peer = target - 2 = 9 - 2 = 7
然后到 d 中去查找 peer=7 是否存在,很明显不存在,那就执行
d[2] = 0就是把 2 这个数字对应的下标 0 保存到哈希表 d 中去。
然后在继续遍历,接下来遍历到 7,计算 peer = target - 7 = 2
然后到 d 中去查找 peer=2 是否存在,发现存在。返回结果。
参考代码:
class Solution: def twoSum(self, nums: List[int], target: int) -> List[int]: d = {} for i, v in enumerate(nums): peer = target - v if peer in d: return [i, d[peer]] else: d[v] = i#include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <map> #include <stdio.h> using namespace std; class Solution { public: vector<int> twoSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) { vector<int> vecResult; map<int, int> mapNumIndex; map<int, int>::iterator mapIter; for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) { int iNum = nums[i]; int iPeerNum = target - iNum; int iIndex = i; mapIter = mapNumIndex.find(iPeerNum); if(mapIter != mapNumIndex.end()) { vecResult.push_back(mapIter->second); vecResult.push_back(iIndex); } else { mapNumIndex.insert( std::pair<int, int>(iNum, iIndex) ); } } return vecResult; } }; int main() { vector<int> nums; nums.push_back(2); nums.push_back(7); nums.push_back(11); nums.push_back(15); Solution oSolution; oSolution.twoSum(nums, 9); return 0; }
-
[Git] git 基础使用
一:创建版本库
1
通过命令 git init 把这个目录变成git可以管理的仓库,如下:
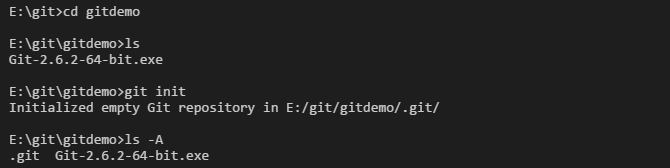
2
把文件添加到版本库中。
第一步:使用命令 git add readme.txt添加到暂存区里面去。如下:
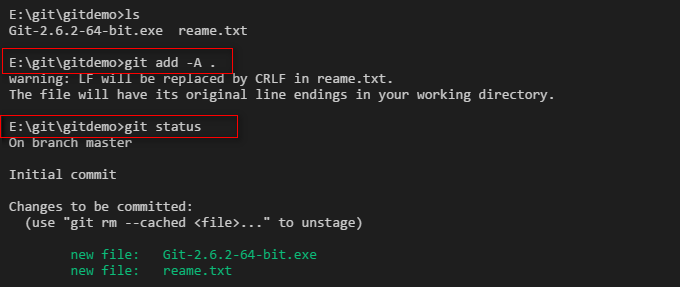
第二步:用命令 git commit告诉Git,把文件提交到仓库。
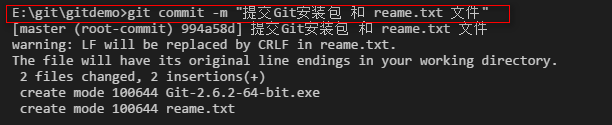
3
修改文件内容。
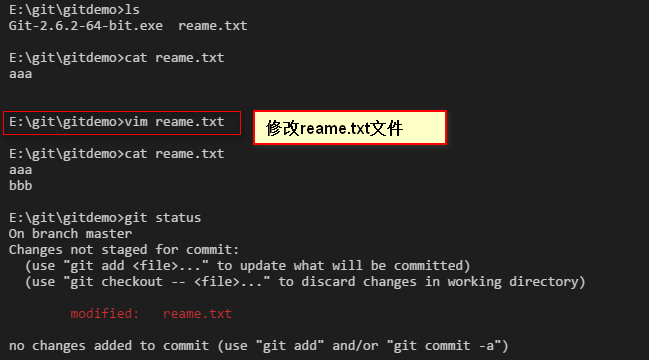
查看具体修改了哪些内容:
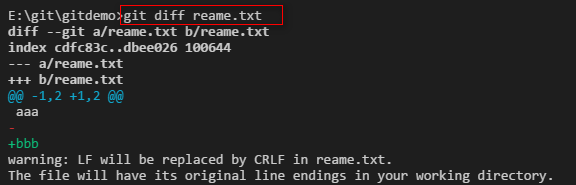
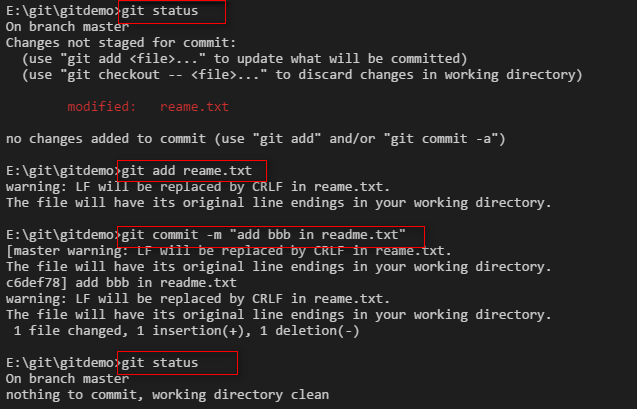
可以看到我们给reame.txt 文件增加了一行bbb内容。然后我们继续把修改的内容提交到版本库。
4
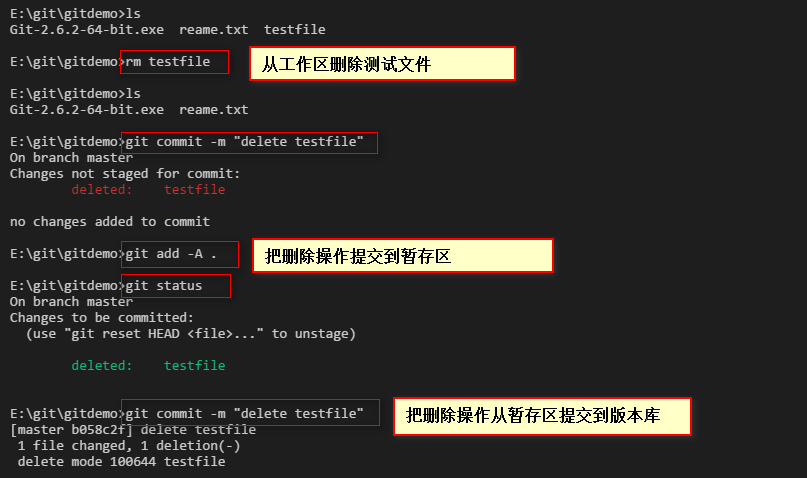
删除文件。
二:版本回退
查看提交的日志。
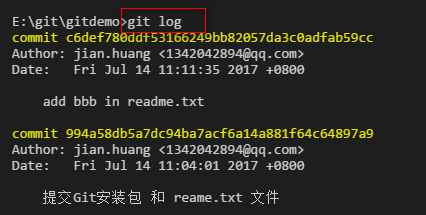
上面的信息太多了,还可以查看简单版的日志:
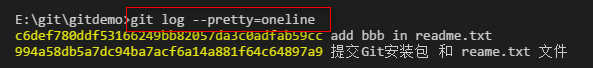
回退到特定的版本:
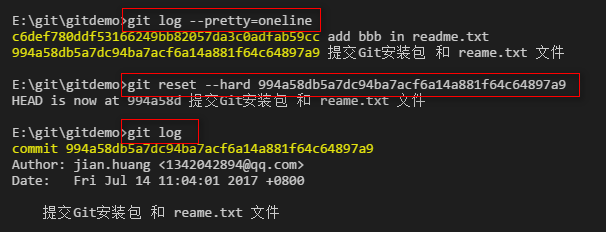
返回到刚才的版本:
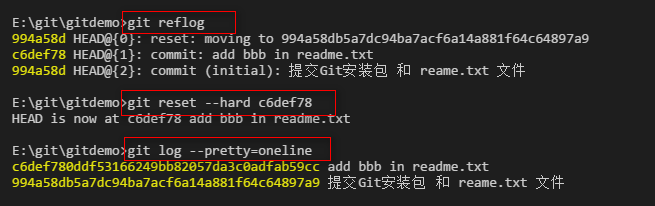
三:理解工作区与暂存区的区别?
工作区:就是你在电脑上看到的目录,比如目录下testgit里的文件(.git隐藏目录版本库除外)。或者以后需要再新建的目录文件等等都属于工作区范畴。
版本库(Repository):工作区有一个隐藏目录.git,这个不属于工作区,这是版本库。其中版本库里面存了很多东西,其中最重要的就是stage(暂存区),还有Git为我们自动创建了第一个分支master,以及指向master的一个指针HEAD。
我们前面说过使用Git提交文件到版本库有两步:
第一步:是使用 git add 把文件添加进去,实际上就是把文件添加到暂存区。
第二步:使用git commit提交更改,实际上就是把暂存区的所有内容提交到当前分支上。
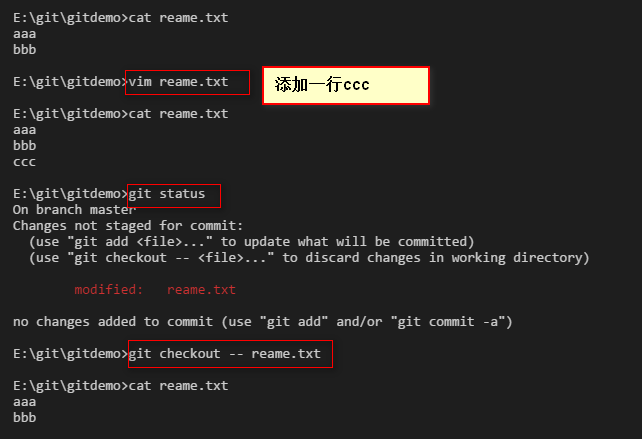
四:Git撤销修改
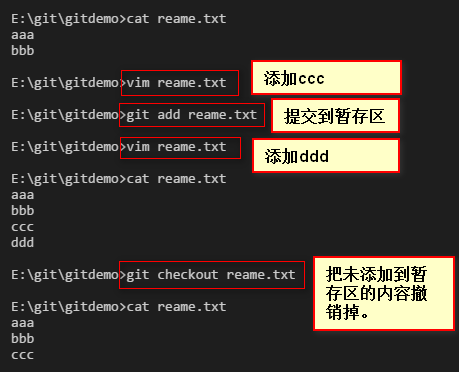
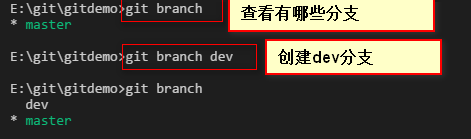
五:分支
在 版本回填退里,你已经知道,每次提交,Git都把它们串成一条时间线,这条时间线就是一个分支。截止到目前,只有一条时间线,在Git里,这个分支叫主分支,即master分支。
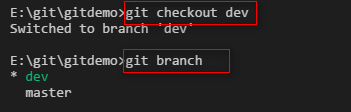
切换到dev分支
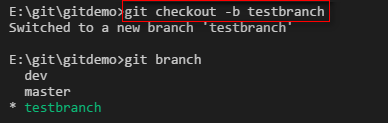
创建testbranch分支,同时切换到testbranch分支上去。
删除分支
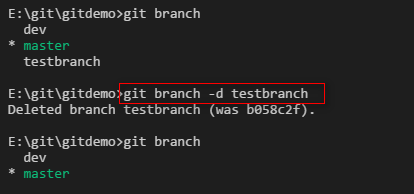
1. 下面举例说明如何使用 分支 来帮助开发。
首先进入master分支,查看readme.txt文件内容,只有aaa,bbb,ccc
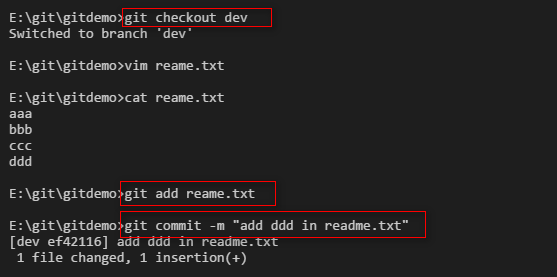
然后切换到dev分支,往readme.txt文件中添加 ddd,并提交修改。
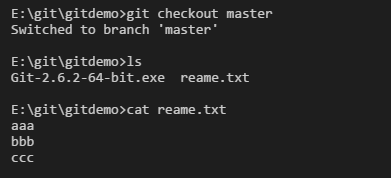
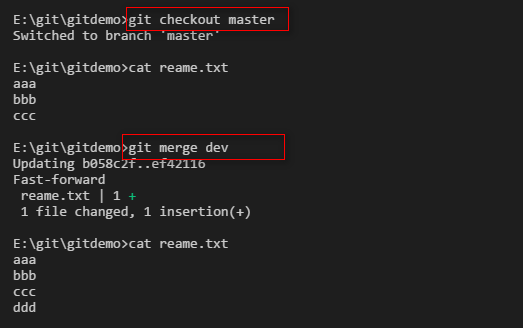
接着切换回master分支,查看reame.txt文件并没有ddd,然后我们执行merge动作,把dev分支merge到master分支上。
分支策略:首先master主分支应该是非常稳定的,也就是用来发布新版本,一般情况下不允许在上面干活,干活一般情况下在新建的dev分支上干活,干完后,比如上要发布,或者说dev分支代码稳定后可以合并到主分支master上来。
2. 合并分支时,如何解决冲突?
先把刚才的分支,东西全部删了。
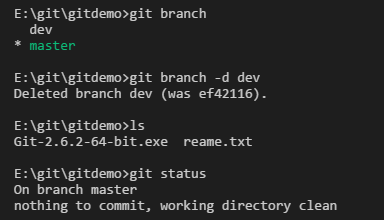
然后创建dev分支,并向readme.txt添加eee,并提交修改。
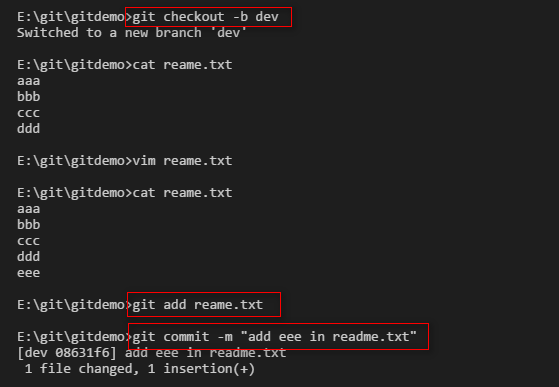
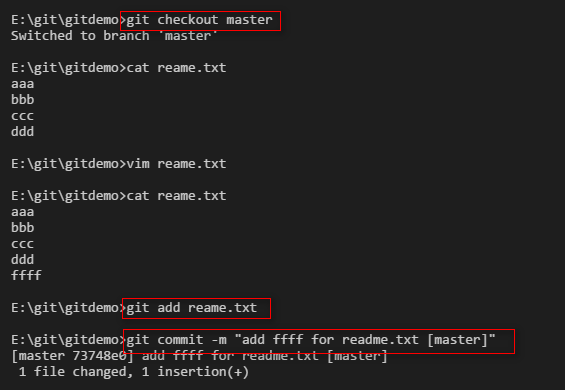
切换到master分支,并向readme.txt添加ffff,并提交修改。
在master分支下执行merge操作,然后readme.txt文件会出现冲突,修改readme.txt文件,修改好了之后提交readme.txt。
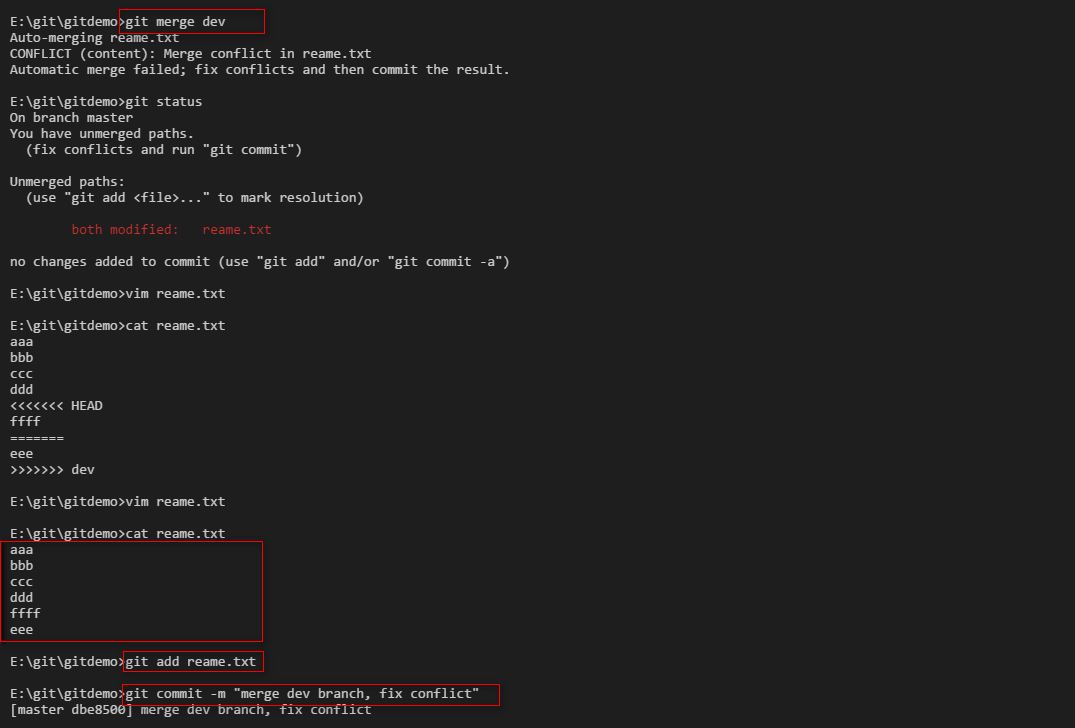
查看merge的日志。
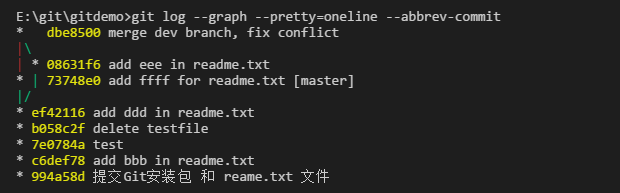
六:远程仓库。
那么如何添加远程库?
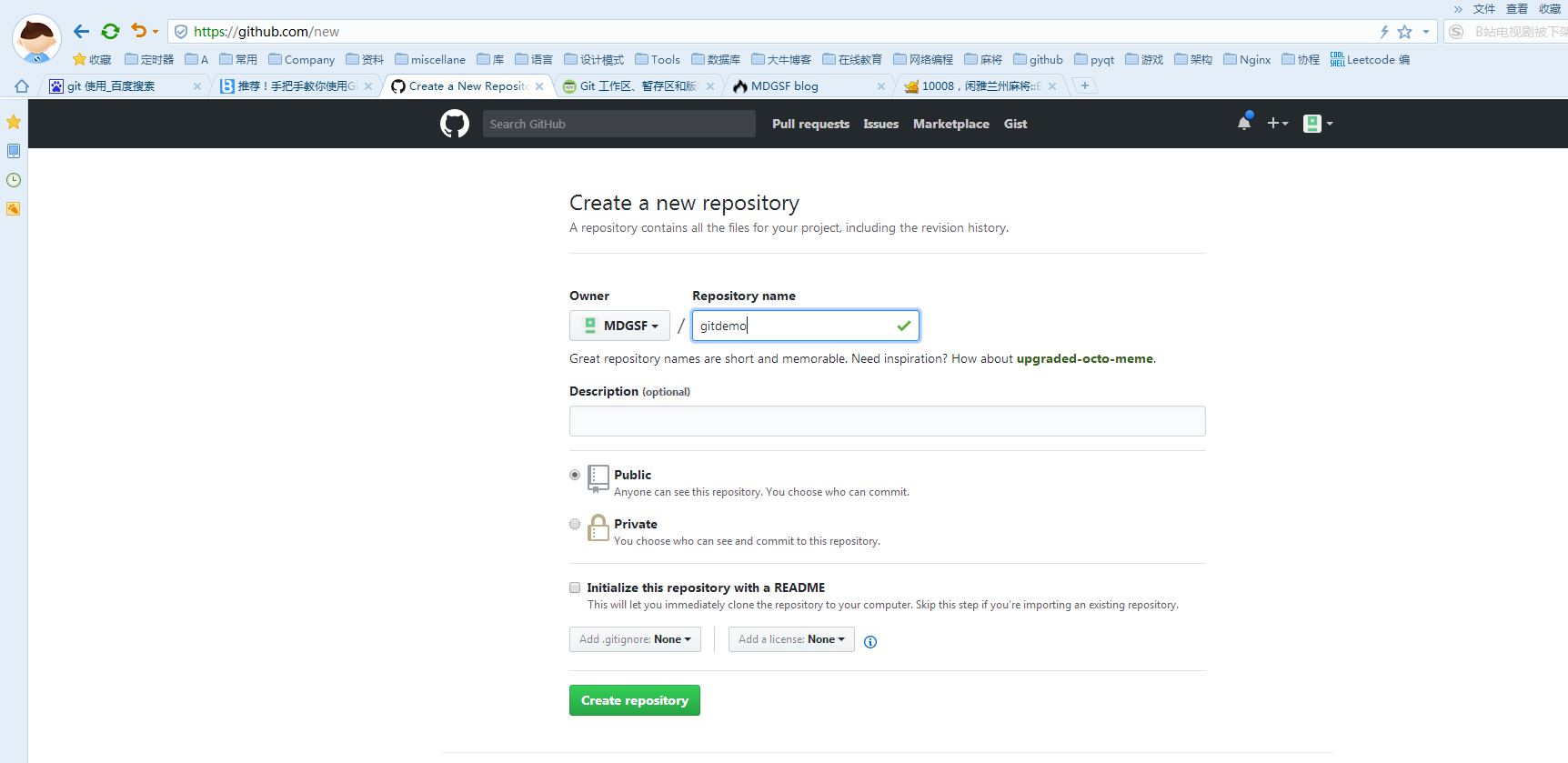
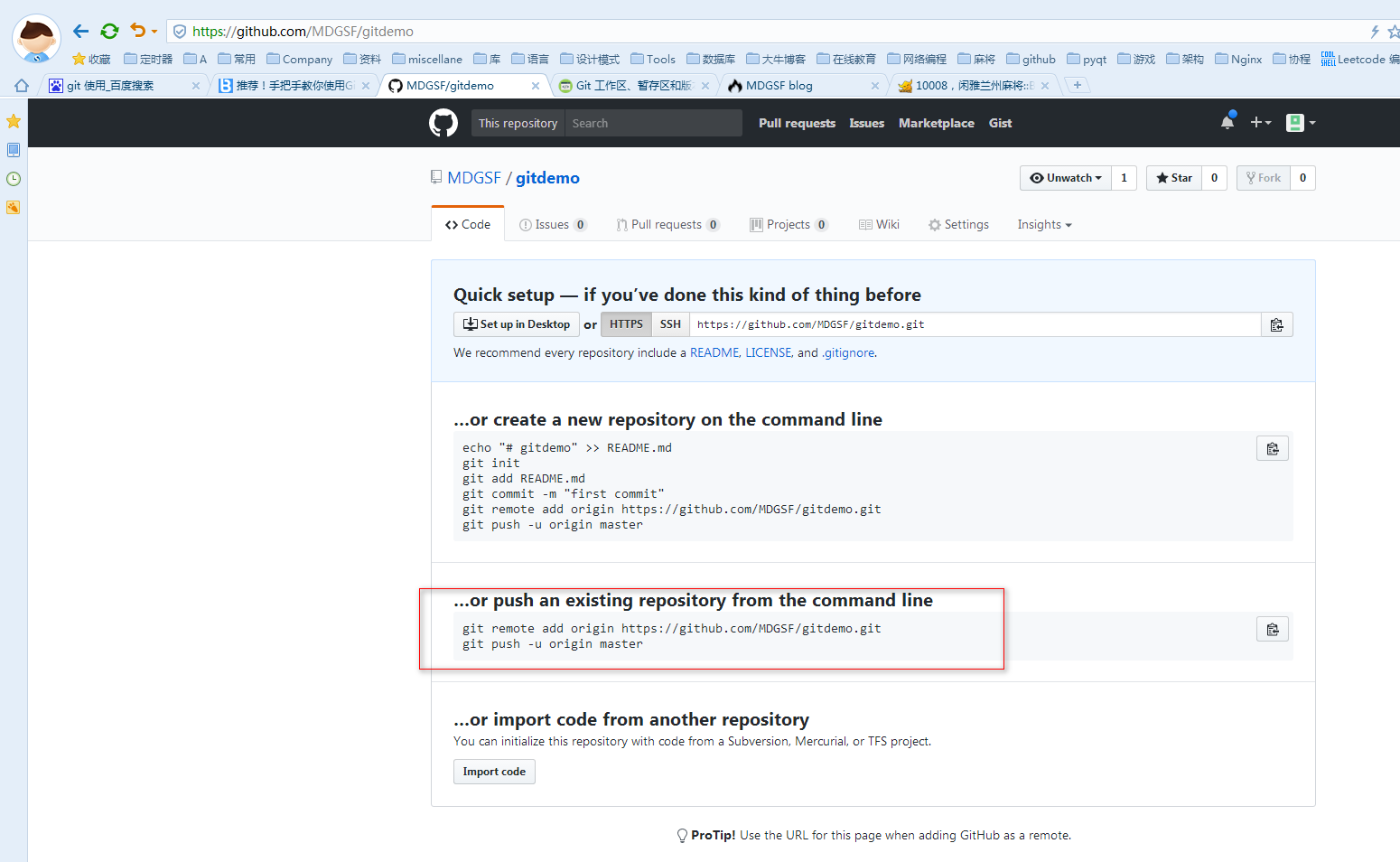
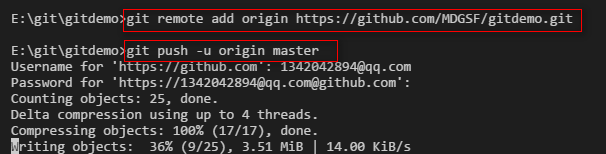
从现在起,只要本地作了提交,就可以通过如下命令:
git push origin master
把本地master分支的最新修改推送到github上了,现在你就拥有了真正的分布式版本库了。
七:.gitignore文件
这个文件的作用就是告诉Git哪些文件不需要添加到版本管理中。
在这个文件里面可以写上编译时生成的中间文件,那么在 git status, git add 的时候,就不会被提交了。
Git基本常用命令如下:
mkdir: XX (创建一个空目录 XX指目录名)
pwd: 显示当前目录的路径。
git init 把当前的目录变成可以管理的git仓库,生成隐藏.git文件。
git add XX 把xx文件添加到暂存区去。
(use “git rm –cached
..." to unstage) 这个命令是用来取消暂存区中的文件的。 git commit –m “XX” 提交文件 –m 后面的是注释。
git status 查看仓库状态
git diff XX 查看XX文件修改了那些内容
git log 查看历史记录
git reset –hard HEAD^ 或者 git reset –hard HEAD~ 回退到上一个版本
(如果想回退到100个版本,使用git reset –hard HEAD~100 )cat XX 查看XX文件内容
git reflog 查看历史记录的版本号id
git checkout — XX 把XX文件在工作区的修改全部撤销。
git rm XX 删除XX文件
git remote add origin https://github.com/tugenhua0707/testgit 关联一个远程库
git push –u(第一次要用-u 以后不需要) origin master 把当前master分支推送到远程库
git clone https://github.com/tugenhua0707/testgit 从远程库中克隆
git checkout –b dev 创建dev分支 并切换到dev分支上
git branch 查看当前所有的分支
git checkout master 切换回master分支
git merge dev 在当前的分支上合并dev分支
git branch –d dev 删除dev分支
git branch name 创建分支
git stash 把当前的工作隐藏起来 等以后恢复现场后继续工作
git stash list 查看所有被隐藏的文件列表
git stash apply 恢复被隐藏的文件,但是内容不删除
git stash drop 删除文件
git stash pop 恢复文件的同时 也删除文件
git remote 查看远程库的信息
git remote –v 查看远程库的详细信息
git push origin master Git会把master分支推送到远程库对应的远程分支上
参考链接
-
[Windows] 切割文件
split -b 45000000 test.log
将文件切割为45M的大小。
- Jekyll 1
- C/C++ 63
- Linux 59
- Web 25
- Qt 12
- Art 124
- Windows 17
- PHP 8
- Network 16
- GDB 3
- lwip 2
- DesignPattern 6
- pthread 6
- CPrimerPlus 9
- tester 3
- GO 75
- openssl 7
- FreeRTOS 9
- 数据库 4
- vk_mj 7
- transdata 3
- Git 7
- lua 20
- nginx 19
- boost 9
- python 18
- google 1
- Redis 1
- miscellanea 11
- life 2
- GCTT 9
- Rust 15
- C语言 2
- TeX 3
- fp 1