Welcome to MDGSF's Blog!
This is my github blog-
[测试][Bugfree] Fix bug时的解决方案选择
By Design:这不是个bug,就是这么设计的
Duplicate:重复的bug
External:外部原因,机器原因,操作原因等待
Fixed:已解决
Not Repro:无法重现
Postponed:推迟解决
Won’t Fix:我知道这是个bug,但是不打算解决,要说明原因
-
[算法学习][leetcode] 53 Maximum Subarray
https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-subarray/description/
题目
Find the contiguous subarray within an array (containing at least one number) which has the largest sum.
For example, given the array [-2,1,-3,4,-1,2,1,-5,4],
the contiguous subarray [4,-1,2,1] has the largest sum = 6.
题目翻译
题目解析
参考答案
int maxSubArray(int* nums, int numsSize) { int i; int iSum = 0; int iAns = -100000000; for (i = 0; i < numsSize; i++) { iSum += nums[i]; if(iSum > iAns) { iAns = iSum; } if(iSum < 0) { iSum = 0; } } return iAns; }iSum 用来保存当前计算的子数组的和
iAns 用来保存最大的子数组的和
如果 iSum < 0, 则这个子数组必定不能作为其它子数组的前缀,所以直接抛弃。
假设 A 为 iSum < 0 的一个子数组, B 为 iSum >= 0 的一个子数组。
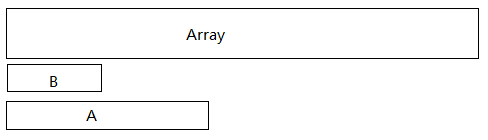
上图这种情况,B作为A的前缀,则B一定被先计算过。当A被抛弃时,B的结果已经被保存到iAns中过了。
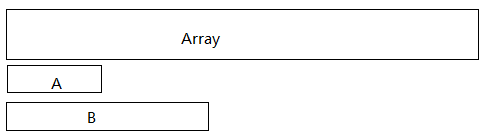
而这种A作为B的前缀,在计算A的时候A就已经被抛弃了。
-
[算法学习][leetcode] 24 Swap Nodes in Pairs
https://leetcode.com/problems/swap-nodes-in-pairs/description/
题目
Given a linked list, swap every two adjacent nodes and return its head.
For example,
Given 1->2->3->4, you should return the list as 2->1->4->3.
Your algorithm should use only constant space. You may not modify the values in the list, only nodes itself can be changed.
题目翻译
题目解析
参考答案
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * struct ListNode *next; * }; */ struct ListNode* swapPairs(struct ListNode* head) { if (NULL == head || NULL == head->next) { return head; } struct ListNode * pCur; struct ListNode * pNext; struct ListNode * pLastTail; pLastTail = head; pCur = head; pNext = pCur->next; while (pCur != NULL && pNext != NULL) { pCur->next = pNext->next; pNext->next = pCur; if(pCur == head) { head = pNext; } else { pLastTail->next = pNext; } pLastTail = pCur; pCur = pCur->next; pNext = pCur != NULL ? pCur->next : NULL; } return head; }
-
[算法学习][leetcode] 21 Merge Two Sorted Lists
https://leetcode.com/problems/merge-two-sorted-lists/description/
题目
Merge two sorted linked lists and return it as a new list. The new list should be made by splicing together the nodes of the first two lists.
题目翻译
题目解析
参考答案
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * struct ListNode *next; * }; */ struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* l1, struct ListNode* l2) { if(NULL == l1 && NULL == l2) { return NULL; } if(NULL == l1) { return l2; } if(NULL == l2) { return l1; } struct ListNode stDump; struct ListNode * pNewHead; pNewHead = &stDump; while (l1 != NULL && l2 != NULL) { if(l1->val < l2->val) { pNewHead->next = l1; l1 = l1->next; } else { pNewHead->next = l2; l2 = l2->next; } pNewHead = pNewHead->next; } if (l1 != NULL) { pNewHead->next = l1; } if(l2 != NULL) { pNewHead->next = l2; } return stDump.next; }
-
[算法学习][leetcode] 19 Remove Nth Node From End of List
https://leetcode.com/problems/remove-nth-node-from-end-of-list/description/
题目
Given a linked list, remove the nth node from the end of list and return its head.
For example,
Given linked list: 1->2->3->4->5, and n = 2. After removing the second node from the end, the linked list becomes 1->2->3->5.Note:
Given n will always be valid.
Try to do this in one pass.
题目翻译
题目解析
参考答案
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: ListNode *removeNthFromEnd(ListNode *head, int n) { int iLen = 0; ListNode * p = head; while(p != NULL) { iLen++; p = p->next; } p = head; for (int i=0; i<iLen-n-1; i++) { p = p->next; } if((p == head) && (n == iLen)) { head = p->next; delete p; return head; } ListNode * pstDel = p->next; if(pstDel->next == NULL) { p->next = NULL; } else { p->next = pstDel->next; } delete pstDel; return head; } };这个方法遍历的2遍。
如果要遍历1遍,则需要拿一个指针p1指向head,p1先向前走n步, 然后再拿一个指针p2指向head,p1和p2同时向前,p1走到尾部时,p2就指向了要删除的节点。
-
[C/C++] 无符号数 和 有符号数 的二进制图
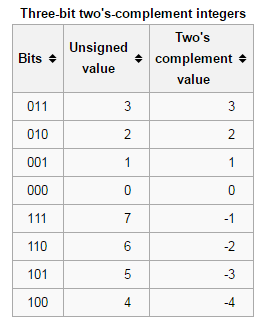
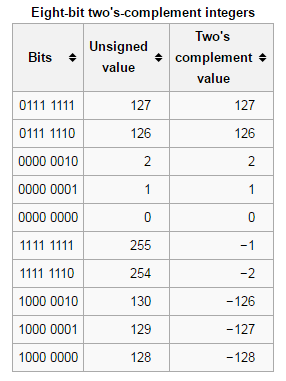
- Jekyll 1
- C/C++ 63
- Linux 59
- Web 25
- Qt 12
- Art 124
- Windows 17
- PHP 8
- Network 16
- GDB 3
- lwip 2
- DesignPattern 6
- pthread 6
- CPrimerPlus 9
- tester 3
- GO 75
- openssl 7
- FreeRTOS 9
- 数据库 4
- vk_mj 7
- transdata 3
- Git 7
- lua 20
- nginx 19
- boost 9
- python 18
- google 1
- Redis 1
- miscellanea 11
- life 2
- GCTT 9
- Rust 15
- C语言 2
- TeX 3
- fp 1