Welcome to MDGSF's Blog!
This is my github blog-
[算法学习][动态规划] 斐波那契数列
斐波那契数列
num: 0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, ... idx: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, ...就是前两个数相加等于第 3 个数。
希望实现一个函数,传入参数 idx 下标,返回对应的 num 数字。
递推公式
fib[n] = fib[n-1] + fib[n-2] fib[0] = 0 fib[1] = 1方法一、简单递归
func fib(n int) int { if n <= 1 { return n } return fib(n-1) + fib(n-2) }时间复杂度: O(2^n)
那为什么时间复杂度是 O(2^n) 呢?
看下面两张图就知道了,fib(4), fib(3), fib(2), fib(1) 都被多次重复计算。
|--F(1) |--F(2)| |--F(3)| |--F(0) | | |--F(4)| |--F(1) | | | | |--F(1) | |--F(2)| | |--F(0) F(5)| | |--F(1) | |--F(2)| | | |--F(0) |--F(3)| | |--F(1)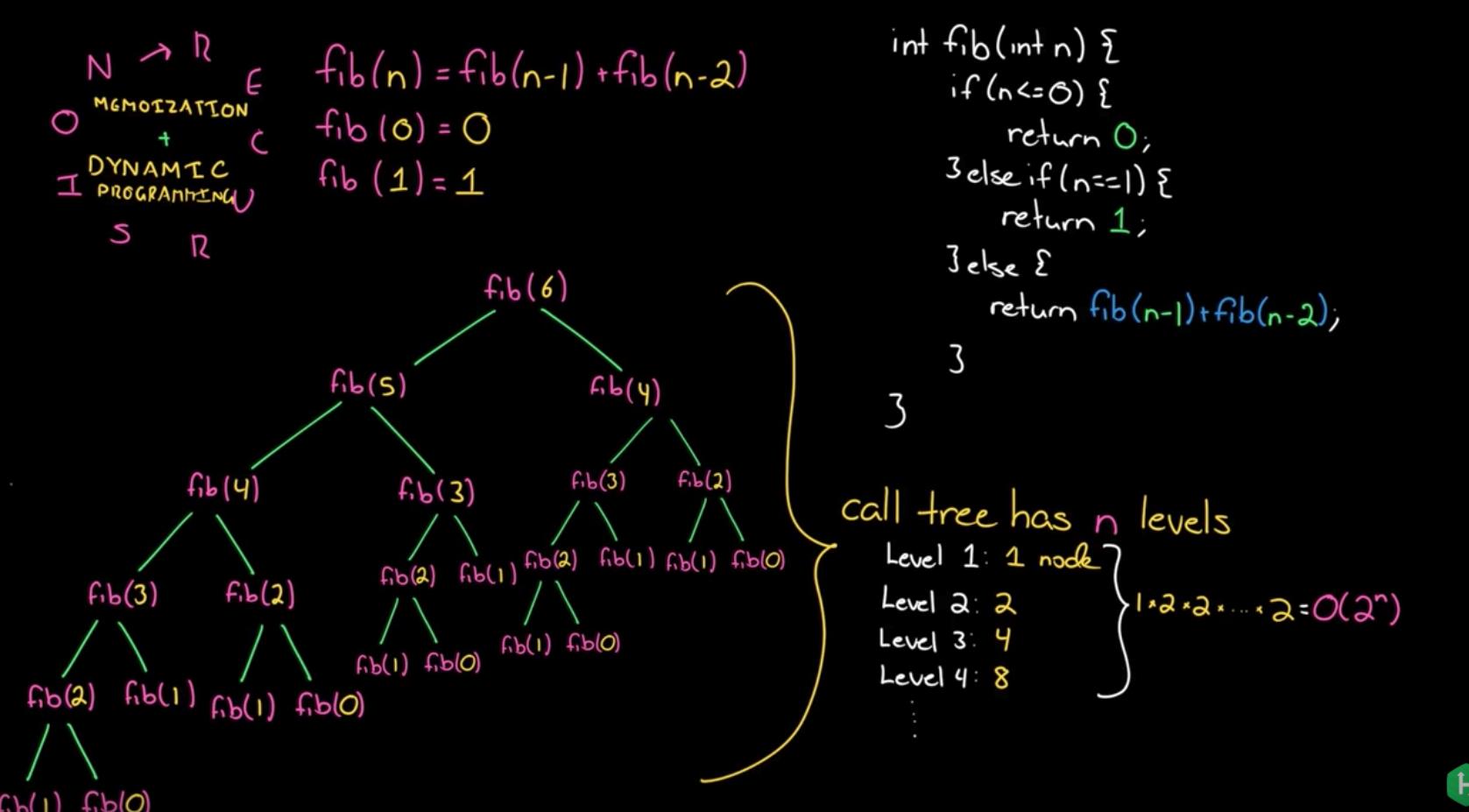
第 1 层: 2^0 第 2 层: 2^1 第 3 层: 2^2 第 4 层: 2^3 第 5 层: 2^4 ...虽然不是一个满二叉树,但是数量级也是 O(2^n) 的。
方法二、简单递归 + 记忆化
记忆化的意思就是说把计算过的值记录下来,防止重复计算。
func fib(n int, m map[int]int) int { if n <= 1 { return n } if _, ok := m[n]; !ok { m[n] = fib(n-1, m) + fib(n-2, m) } return m[n] }时间复杂度:O(n)

方法三、递推
递推其实就只是把递归的代码修改为用循环实现。递推的顺序是和递归正好相反的。func fib(n int) int { if n <= 1 { return n } i, j := 0, 1 for idx := 2; idx <= n; idx++ { i, j = j, i+j } return j }时间复杂度:O(n)
方法四、查表法
如果 n 不是很大的话,我们可以考虑事先计算好所有结果,保存起来。然后直接查表即可。
假设 n = 10000, 每个数字 4 个字节,那么一共需要空间 40000 Byte = 40 KB。
方法五、通项公式
斐波那契数列通项公式:
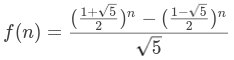
这个是数学上的方法了。
时间复杂度:O(1)
-
[Rust] string type change
use std::mem; use std::str; fn main() { data_type(); string_type(); } fn string_type() { println!("\nhello string: {:?}", "hello world"); println!("hello byte string: {:?}", b"hello world"); let array_of_u8 = [104, 101, 108, 108, 111, 32, 119, 111, 114, 108, 100]; println!("array_of_u8 = {:?}", array_of_u8); // [u8] to String let string_utf8_lossy = String::from_utf8_lossy(&array_of_u8); println!("string_utf8_lossy = {}", string_utf8_lossy); // [u8] to String let mut vec_of_u8 = vec![]; vec_of_u8.extend_from_slice(&array_of_u8); let string_utf8_result = String::from_utf8(vec_of_u8).unwrap(); println!("string_utf8_result = {}", string_utf8_result); // [u8] to str let str_utf8_result = str::from_utf8(&array_of_u8).unwrap(); println!("str_utf8_result = {}", str_utf8_result); // [u8] to Vec<char> let vec_of_chars: Vec<char> = array_of_u8.iter().map(|byte| *byte as char).collect(); println!("vec_of_chars = {:?}", vec_of_chars); // Vec<char> to Vec<u8> let vec_of_u8s: Vec<u8> = vec_of_chars.iter().map(|c| *c as u8).collect(); println!("vec_of_u8s = {:?}", vec_of_u8s); // Vec<char> to String let mut string_of_collected_chars: String = vec_of_chars.iter().collect(); println!("string_of_collected_chars = {}", string_of_collected_chars); string_of_collected_chars.push('!'); string_of_collected_chars.push_str("!!"); println!("string_of_collected_chars = {}", string_of_collected_chars); // String to str let str_slice = &string_of_collected_chars[..]; println!("str_slice = {}", &str_slice); // String to [u8] let array_of_u8_from_string = string_of_collected_chars.as_bytes(); println!("array_of_u8_from_string = {:?}", array_of_u8_from_string); // String to Vec<char> let vec_of_chars_from_string: Vec<char> = string_of_collected_chars.chars().collect(); println!("vec_of_chars_from_string = {:?}", vec_of_chars_from_string); // merge string let concat_strings = vec!["abc".to_string(), "def".to_string()].concat(); println!("concat_strings = {}", concat_strings); let joined_strings = vec!["abc".to_string(), "def".to_string()].join("---"); println!("joined_strings = {}", joined_strings); // str to String let a = "hello world"; let b = "ok!"; let c = a.to_string(); let d = String::from(b); let e = a.to_owned(); println!("a = {}", a); println!("b = {}", b); println!("c = {}", c); println!("d = {}", d); println!("e = {}", e); // String + &str ==> String let f = c + " --- " + b; println!("f = {}", f); // f32 + String ==> String let num = 2019_u32; let new_year = String::from(", happy new year"); let num_str = format!("{0}{1}", num, new_year); println!("num_str = {}", num_str); // char to String let single_char: char = 'a'; let string_from_char: String = single_char.to_string(); println!("single_char = {}", single_char); println!("string_from_char = {}", string_from_char); // i32 to String let single_i32: i32 = 32; let string_from_i32: String = single_i32.to_string(); println!("string_from_i32 = {}", string_from_i32); // String to i32 // let i32_from_string: i32 = string_from_i32.parse().unwrap(); // let i32_from_string = string_from_i32.parse::<i32>().unwrap(); let i32_from_string: i32 = string_from_i32.parse::<i32>().unwrap(); println!("i32_from_string = {}", i32_from_string); // vec<&str> to vec<String> let v = vec!["huangjian", "minieye"]; let vec_string = vec_str_to_vec_string(v); println!("vec_string = {:?}", vec_string); } fn vec_str_to_vec_string(strs: Vec<&str>) -> Vec<String> { println!("strs = {:?}", strs); let mut result = Vec::new(); for i in &strs { result.push((*i).to_string()); } result } fn data_type() { println!("Show Data Type"); let single_i8: i8 = 8; let single_i16: i16 = 16; let single_i32: i32 = 32; let single_i64: i64 = 64; let single_i128: i128 = 128; println!("single_i8 = {}", single_i8); println!("single_i16 = {}", single_i16); println!("single_i32 = {}", single_i32); println!("single_i64 = {}", single_i64); println!("single_i128 = {}", single_i128); let single_u8: u8 = 8; let single_u16: u16 = 16; let single_u32: u32 = 32; let single_u64: u64 = 64; let single_u128: u128 = 128; println!("single_u8 = {}", single_u8); println!("single_u16 = {}", single_u16); println!("single_u32 = {}", single_u32); println!("single_u64 = {}", single_u64); println!("single_u128 = {}", single_u128); println!("Decimal = {}", 98_222); println!("Hex = {}", 0xff); println!("Octal = {}", 0o77); println!("Binary = {}", 0b1111_0000); println!("Byte(u8) = {}", b'A'); let single_f32: f32 = 32.0; let single_f64: f64 = 64.0; println!("single_f32 = {}", single_f32); println!("single_f64 = {}", single_f64); // i32 to i64 let i64_from_i32 = single_i32 as i64; println!("i64_from_i32 = {}", i64_from_i32); // i32 to u32 let u32_from_i32 = single_i32 as u32; println!("u32_from_i32 = {}", u32_from_i32); // i32 to f64 let f64_from_i32 = single_i32 as f64; println!("f64_from_i32 = {}", f64_from_i32); // transmute is dangerous. unsafe { let a = [127u8, 0u8, 0u8, 1u8]; let b = mem::transmute::<[u8; 4], u32>(a); println!("b_transmute_from_a = {}", b); } }
-
[算法学习] Manacher Algorithm
Question
Given a string, find the longest substring which is palindrome.
Answer
https://github.com/MDGSF/GoPractice/blob/master/a/4/main.go
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/manachers-algorithm-linear-time-longest-palindromic-substring-part-1
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/manachers-algorithm-linear-time-longest-palindromic-substring-part-2/
-
[算法学习] 面试题收集1
题目描述
给你一个数列和一个随机数字 A,你可以把数列中的每一个数字加上这个随机数字 A 或者减去这个随机数字 A,必须加上或者减去,不能不操作。问:要怎么样才能让操作之后的数列中的最大值和最小值间的距离最小。
举个例子:
数列:1 2 3 4 5 随机数字A:11 + 1 = 2 2 + 1 = 3 3 + 1 = 4 4 - 1 = 3 5 - 1 = 4 于是我就得到 新的数列:2 3 4 3 4 最大值和最小值的距离就是 21 + 1 = 2 2 + 1 = 3 3 + 1 = 4 4 + 1 = 5 5 + 1 = 6 于是我就得到 新的数列:2 3 4 5 6 最大值和最小值的距离就是 4
-
copy on write
实现 copy on write 的两个方法
1. 自己实现一个有 copy on write 的数据结构,比如:
https://github.com/google/btree
2. 使用 fork()
https://github.com/MDGSF/CPractice/blob/master/forkDemo/main.cpp
-
[proxy 代理] cow
https://github.com/cyfdecyf/cow
local ~/.cow/rc listen = http://127.0.0.1:7777 proxy = cow://aes-128-cfb:proxy1_password@111.222.333.444:5555 nohup cow &proxy1 listen = cow://aes-128-cfb:proxy1_password@0.0.0.0:5555 proxy = ss://aes-256-cfb:proxy2_password@proxy2_ip_addr:443 nohup cow &proxy2 run shadowsocks server
- Jekyll 1
- C/C++ 63
- Linux 59
- Web 25
- Qt 12
- Art 124
- Windows 17
- PHP 8
- Network 16
- GDB 3
- lwip 2
- DesignPattern 6
- pthread 6
- CPrimerPlus 9
- tester 3
- GO 75
- openssl 7
- FreeRTOS 9
- 数据库 4
- vk_mj 7
- transdata 3
- Git 7
- lua 20
- nginx 19
- boost 9
- python 18
- google 1
- Redis 1
- miscellanea 11
- life 2
- GCTT 9
- Rust 15
- C语言 2
- TeX 3
- fp 1