Welcome to MDGSF's Blog!
This is my github blog-
[Linux] iptables 基础
一. 介绍
iptables 实际上由两个组件netfilter 和 iptables 组成。
-
netfilter 组件也称为内核空间(kernelspace),是内核的一部分,由一些信息包过滤表组成, 这些表包含内核用来控制信息包过滤处理的规则集。
-
iptables 组件是一种工具,也称为用户空间(userspace),它使插入、修改和除去信息包过滤表中的规则变得容易。
netfilter/iptables 的最大优点是它可以配置有状态的防火墙, 这是 ipfwadm 和 ipchains 等以前的工具都无法提供的一种重要功能。 有状态的防火墙能够指定并记住为发送或接收信息包所建立的连接的状态。 防火墙可以从信息包的连接跟踪状态获得该信息。在决定新的信息包过滤时, 防火墙所使用的这些状态信息可以增加其效率和速度。这里有四种有效状态, 名称分别为 ESTABLISHED 、 INVALID 、 NEW 和 RELATED。
ESTABLISHED 指出该信息包属于已建立的连接,该连接一直用于发送和接收信息包并且完全有效。 INVALID 状态指出该信息包与任何已知的流或连接都不相关联,它可能包含错误的数据或头。 NEW 意味着该信息包已经或将启动新的连接,或者它与尚未用于发送和接收信息包的连接相关联。 RELATED 表示该信息包正在启动新连接,以及它与已建立的连接相关联。ACCEPT – 允许防火墙接收数据包 DROP – 防火墙丢弃包 QUEUE – 防火墙将数据包移交到用户空间 RETURN – 防火墙停止执行当前链中的后续Rules,并返回到调用链(the calling chain)中。二. iptables 表,链
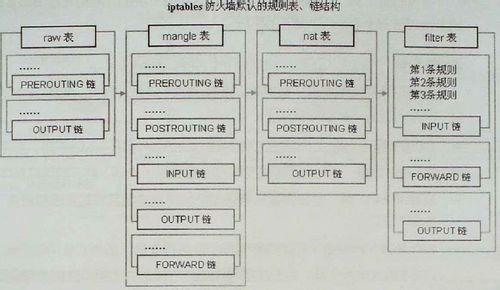
iptables 有4个內建表,5个规格链
2.1 4个內建表
-
filter 表, filter 表 是iptables的默认表
-
nat 表, 这个表被查询时表示遇到了产生新的连接的包
-
mangle 表, 这个表用来对指定的包进行修改。它能改变TCP头中的QoS位。
-
raw 表, Raw表用于处理异常。
2.2 5个规则链
1.PREROUTING (路由前) 2.INPUT (数据包流入口) 3.FORWARD (转发管卡) 4.OUTPUT(数据包出口) 5.POSTROUTING(路由后)2.3 小扩展
对于filter来讲一般只能做在3个链上:INPUT ,FORWARD ,OUTPUT
对于nat来讲一般也只能做在3个链上:PREROUTING ,OUTPUT ,POSTROUTING
而mangle则是5个链都可以做:PREROUTING,INPUT,FORWARD,OUTPUT,POSTROUTING
三. iptables 命令
3.1 查看 filter 表的信息
iptables -L -n -v 默认就是 filter 表 iptables -L -n -v -t filter命令参数:
--list -L [chain [rulenum]] List the rules in a chain or all chains --numeric -n numeric output of addresses and ports --verbose -v verbose mode输出:
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 60650 packets, 5561K bytes) pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT 9443 packets, 1021K bytes) pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 4349 packets, 947K bytes) pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination查看其它的表:
iptables -L -n -v -t nat iptables -L -n -v -t mangle iptables -L -n -v -t raw参数:
--table -t table table to manipulate (default: `filter')3.2 清空iptables
iptables -F iptables -X iptables -Z iptables -P INPUT ACCEPT iptables -P OUTPUT ACCEPT iptables -P FORWARD ACCEPT四. iptables 帮助文档
使用命令:
iptables -hiptables v1.4.21 Usage: iptables -[ACD] chain rule-specification [options] iptables -I chain [rulenum] rule-specification [options] iptables -R chain rulenum rule-specification [options] iptables -D chain rulenum [options] iptables -[LS] [chain [rulenum]] [options] iptables -[FZ] [chain] [options] iptables -[NX] chain iptables -E old-chain-name new-chain-name iptables -P chain target [options] iptables -h (print this help information) Commands: Either long or short options are allowed. --append -A chain Append to chain --check -C chain Check for the existence of a rule --delete -D chain Delete matching rule from chain --delete -D chain rulenum Delete rule rulenum (1 = first) from chain --insert -I chain [rulenum] Insert in chain as rulenum (default 1=first) --replace -R chain rulenum Replace rule rulenum (1 = first) in chain --list -L [chain [rulenum]] List the rules in a chain or all chains --list-rules -S [chain [rulenum]] Print the rules in a chain or all chains --flush -F [chain] Delete all rules in chain or all chains --zero -Z [chain [rulenum]] Zero counters in chain or all chains --new -N chain Create a new user-defined chain --delete-chain -X [chain] Delete a user-defined chain --policy -P chain target Change policy on chain to target --rename-chain -E old-chain new-chain Change chain name, (moving any references) Options: --ipv4 -4 Nothing (line is ignored by ip6tables-restore) --ipv6 -6 Error (line is ignored by iptables-restore) [!] --protocol -p proto protocol: by number or name, eg. `tcp' [!] --source -s address[/mask][...] source specification [!] --destination -d address[/mask][...] destination specification [!] --in-interface -i input name[+] network interface name ([+] for wildcard) --jump -j target target for rule (may load target extension) --goto -g chain jump to chain with no return --match -m match extended match (may load extension) --numeric -n numeric output of addresses and ports [!] --out-interface -o output name[+] network interface name ([+] for wildcard) --table -t table table to manipulate (default: `filter') --verbose -v verbose mode --wait -w wait for the xtables lock --line-numbers print line numbers when listing --exact -x expand numbers (display exact values) [!] --fragment -f match second or further fragments only --modprobe=<command> try to insert modules using this command --set-counters PKTS BYTES set the counter during insert/append [!] --version -V print package version.参考链接
-
-
[Qt] qtcreator 中打开console
(1) qtcreator–>左侧Projects–>Run–>中间的checkbox (Run in terminal)打上勾
(2) 在项目的.pro文件中加上 “CONFIG += console”
-
[Qt] QString 和 char* 转换
(1) QString 转 char*
char acResult[10240]; //QByteArray baResult = strResult.toLatin1(); QByteArray baResult = strResult.toLocal8Bit(); char *pcResult = baResult.data(); strcpy(acResult, pcResult);(2) char* 转QString
char acName[] = "huang"; QString strName = QString(QLatin1String(acName)); QString strName = QString::fromUtf8(acName);
-
A Simple C++ template
#include <stdio.h> //#define FILE //#define DEBUG #ifdef DEBUG #define LOG_PRINTF(format, ...) \ printf("<"__FILE__">(%05d): "format"", __LINE__, ##__VA_ARGS__) #else #define LOG_PRINTF(format, ...) #endif int main() { #ifdef FILE freopen("data.in", "r", stdin); freopen("data.out", "w", stdout); #endif LOG_PRINTF("Hello world!\n"); return 0; }
-
[C/C++] strlen 库函数实现
int strlen(const char *pcStr) { assert(pcStr != NULL); int iLen = 0; while (*pcStr++ != '\0') { iLen++; } return iLen; }
-
[C/C++] strcpy 库函数实现
char * strcpy(char *to, char *from) { assert((to != NULL) && (from != NULL)); char *save = to; for (; (*to = *from) != '\0'; ++from, ++to) { } return save; }
- Jekyll 1
- C/C++ 63
- Linux 59
- Web 25
- Qt 12
- Art 124
- Windows 17
- PHP 8
- Network 16
- GDB 3
- lwip 2
- DesignPattern 6
- pthread 6
- CPrimerPlus 9
- tester 3
- GO 75
- openssl 7
- FreeRTOS 9
- 数据库 4
- vk_mj 7
- transdata 3
- Git 7
- lua 20
- nginx 19
- boost 9
- python 18
- google 1
- Redis 1
- miscellanea 11
- life 2
- GCTT 9
- Rust 15
- C语言 2
- TeX 3
- fp 1